OpenTracingチュートリアルをやってみた(その1)
OpenTracingチュートリアルをやったメモ
OpenTracingとは
OpenTracingは、API仕様とそれを実装したフレームワークとライブラリ、およびプロジェクトのドキュメントで構成されています。 OpenTracingを使用すると、開発者は特定の製品やベンダーにロックされていないAPIを使用してアプリケーションコードにトレーシング機能を追加できます。
OpenTracingがサポートしている言語
- Go, JavaScript, Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, Objective-C, C++, C#
OpenTracingチュートリアル
このチュートリアルではTracerとしてJaegerを使用しています。
Jaegerとは
DapperとOpenZipkinにインスパイヤーされUber TechnologiesによってリリースされたオープンソースのOpenTracing互換の分散トレースシステムです。
アーキテクチャはこのような感じです。

Architecture — Jaeger documentation
Client以外の起動に関してはAll-in-oneのDockerイメージが公開されているのでそれを使用すれば起動できます。 Getting started — Jaeger documentation
今回は必要最低限のポートのみを指定して起動します。
docker run --rm -p 6831:6831/udp -p 6832:6832/udp -p 16686:16686 jaegertracing/all-in-one:1.8 --log-level=debug
簡単なトレースを作成してみる
まずはLesson 1 - Hello Worldから。
- TracerはJaegerを初期化しJaegerTracerを取得します。
buildSpan()を使用してオペレーション名を設定しSpanBuilderを生成します。(今回は"say-hello"と設定)spanはstart()を使用して生成しfinish()を使用し終了する必要があります。spanの開始と終了のタイムスタンプは、Tracerの実装(Jaeger)によって自動的に取得されます。
import io.jaegertracing.Configuration; import io.jaegertracing.Configuration.ReporterConfiguration; import io.jaegertracing.Configuration.SamplerConfiguration; import io.jaegertracing.internal.JaegerTracer; import io.opentracing.Span; import io.opentracing.Tracer; public class Hello { private final Tracer tracer; public Hello(Tracer tracer) { this.tracer = tracer; } public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length != 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); Tracer tracer = initTracer("hello-world"); new Hello(tracer).sayHello(args[0]); } private void sayHello(String helloTo) { Span span = tracer.buildSpan("say-hello").start(); String helloStr = String.format("Hello, %s", helloTo); System.out.println(helloStr); span.finish(); } private static JaegerTracer initTracer(String service) { SamplerConfiguration samplerConfiguration = SamplerConfiguration.fromEnv().withType("const").withParam(1); ReporterConfiguration reporterConfiguration = ReporterConfiguration.fromEnv().withLogSpans(true); Configuration configuration = new Configuration(service).withSampler(samplerConfiguration).withReporter(reporterConfiguration); return configuration.getTracer(); } }
上記で分かるように、Tracer、Spanに関してはOpenTracingによって仕様が切られている為OpenTracingのinterfaceを使用し実装に関してはJaegerを使用していることが分かります。
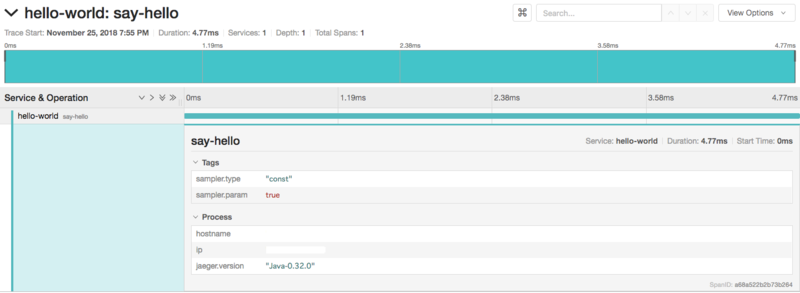
トレースにTagとLogを付ける
- Tag
- Log
- Spanに関連づけられるログステートメント
OpenTracing仕様には、推奨されるTagとLogフィールドの セマンティック規約と呼ばれるガイドラインがあります。
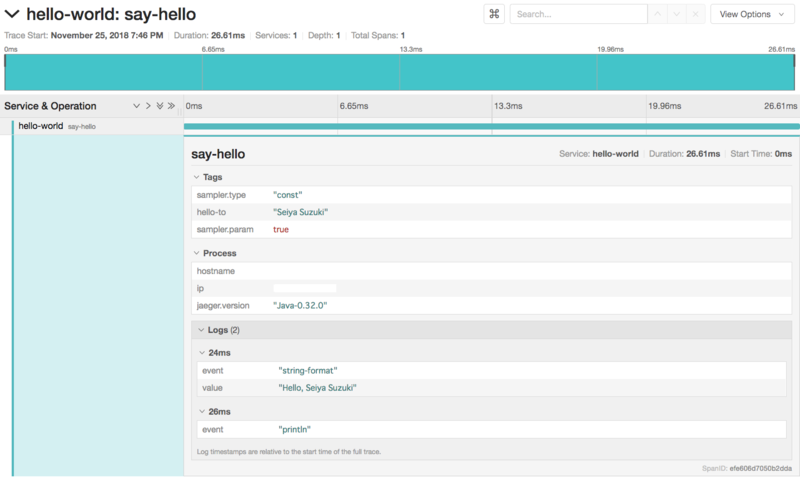
Hello, Hoge!の場合に引数の"Hoge"はSpan全体に適用される為、Tagとして記録します。- このプログラムでは引数をフォーマットしてからprintlnしています。この両方の操作には一定の時間がかかるので、その完了をLogとして記録します。
public class Hello { private final Tracer tracer; public Hello(Tracer tracer) { this.tracer = tracer; } public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length != 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); Tracer tracer = initTracer("hello-world"); new Hello(tracer).sayHello(args[0]); } private void sayHello(String helloTo) { Span span = tracer.buildSpan("say-hello").start(); // Tagの記録 span.setTag("hello-to", helloTo); String helloStr = String.format("Hello, %s", helloTo); // Logの記録 span.log(ImmutableMap.of("event", "string-format", "value", helloStr)); System.out.println(helloStr); // Logの記録 span.log(ImmutableMap.of("event", "println")); span.finish(); } private static JaegerTracer initTracer(String service) { SamplerConfiguration samplerConfiguration = SamplerConfiguration.fromEnv().withType("const").withParam(1); ReporterConfiguration reporterConfiguration = ReporterConfiguration.fromEnv().withLogSpans(true); Configuration configuration = new Configuration(service).withSampler(samplerConfiguration).withReporter(reporterConfiguration); return configuration.getTracer(); } }
個別機能をトレースする
次はLesson 2 - Context and Tracing Functionsを。
- 文字列のフォーマットと出力を個別のメソッドに分けます。
buildSpan()の追加オプションasChildOf()を使用し、個別に分けたメソッドのSpanをmain()メソッドのSpanの子Spanにします。
public class Hello { private final Tracer tracer; public Hello(Tracer tracer) { this.tracer = tracer; } public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length != 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); Tracer tracer = initTracer("hello-world"); new Hello(tracer).sayHello(args[0]); } private void sayHello(String helloTo) { Span span = tracer.buildSpan("say-hello").start(); span.setTag("hello-to", helloTo); String helloStr = formatString(span, helloTo); printHello(span, helloStr); span.finish(); } private String formatString(Span rootSpan, String helloTo) { Span span = tracer.buildSpan("formatString").asChildOf(rootSpan).start(); try { String helloStr = String.format("Hello, %s", helloTo); span.log(ImmutableMap.of("event", "string-format", "value", helloStr)); return helloStr; } finally { span.finish(); } } private void printHello(Span rootSpan, String helloStr) { Span span = tracer.buildSpan("printHello").asChildOf(rootSpan).start(); try { System.out.println(helloStr); span.log(ImmutableMap.of("event", "println")); } finally { span.finish(); } } private static JaegerTracer initTracer(String service) { Configuration.SamplerConfiguration samplerConfiguration = Configuration.SamplerConfiguration.fromEnv().withType("const").withParam(1); Configuration.ReporterConfiguration reporterConfiguration = Configuration.ReporterConfiguration.fromEnv().withLogSpans(true); Configuration configuration = new Configuration(service).withSampler(samplerConfiguration).withReporter(reporterConfiguration); return configuration.getTracer(); } }

"active span"を使用
上記のコードで幾つか面倒なところが有りました。
- 各関数の最初の引数としてSpanオブジェクトを渡さなければなりませんでした
- スパンを完成させるためにやや冗長なtry / finallyコードを書く必要もありました
OpenTracing API for Javaではスレッドローカルと"active span"という概念を使用することで、Spanをコードに渡すことなくTracer経由でアクセスすることができます。
start()ではなくbuildSpan()のstartActive()メソッドを使用して、スレッドローカルに格納してSpanをアクティブにします。startActive()はSpanではなくScopeオブジェクトを返します。Scopeは現在アクティブなSpanのコンテナです。scope.span()を介してアクティブなSpanにアクセスします。Scopeを閉じると以前のScopeが現在のScopeになり、現在アクティブなスレッドのSpanを再びアクティブにします。Scopeは自動クローズ可能で、try-with-resource構文を使用できます。startActive(true)はスコープを閉じるとスパンを終了します。startActive()はアクティブSpanへのChildOf参照を自動的に作成するため、buildSpanのasChildOf()を使用する必要はありません。
public class Hello { private final Tracer tracer; public Hello(Tracer tracer) { this.tracer = tracer; } public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length != 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); Tracer tracer = initTracer("hello-world"); new Hello(tracer).sayHello(args[0]); } private void sayHello(String helloTo) { try (Scope scope = tracer.buildSpan("say-hello").startActive(true)) { scope.span().setTag("hello-to", helloTo); String helloStr = formatString(helloTo); printHello(helloStr); } } private String formatString(String helloTo) { try (Scope scope = tracer.buildSpan("formatString").startActive(true)) { String helloStr = String.format("Hello, %s", helloTo); scope.span().log(ImmutableMap.of("event", "string-format", "value", helloStr)); return helloStr; } } private void printHello(String helloStr) { try (Scope scope = tracer.buildSpan("printHello").startActive(true)) { System.out.println(helloStr); scope.span().log(ImmutableMap.of("event", "println")); } } private static JaegerTracer initTracer(String service) { Configuration.SamplerConfiguration samplerConfiguration = Configuration.SamplerConfiguration.fromEnv().withType("const").withParam(1); Configuration.ReporterConfiguration reporterConfiguration = Configuration.ReporterConfiguration.fromEnv().withLogSpans(true); Configuration configuration = new Configuration(service).withSampler(samplerConfiguration).withReporter(reporterConfiguration); return configuration.getTracer(); } }
次回は残りのLesson 03 、Lesson 04をしたいと思います。